PDT by Example
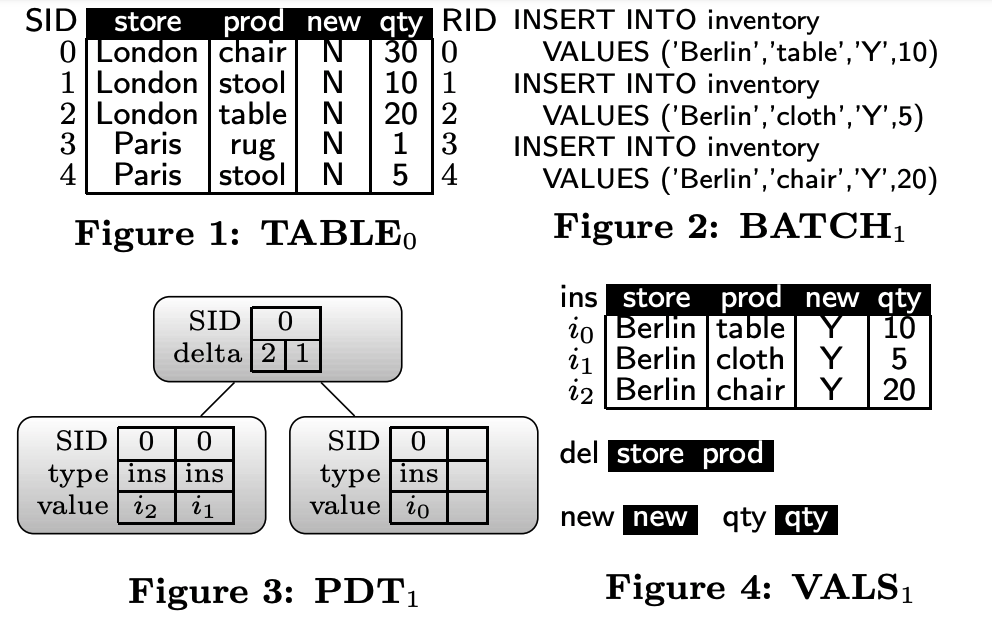
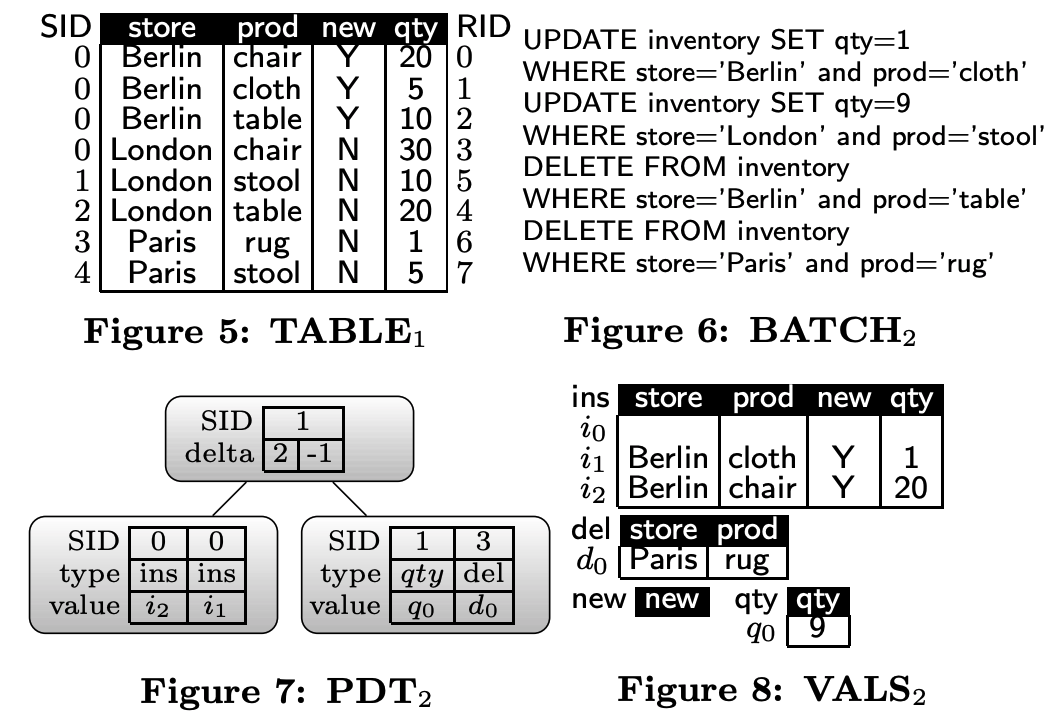
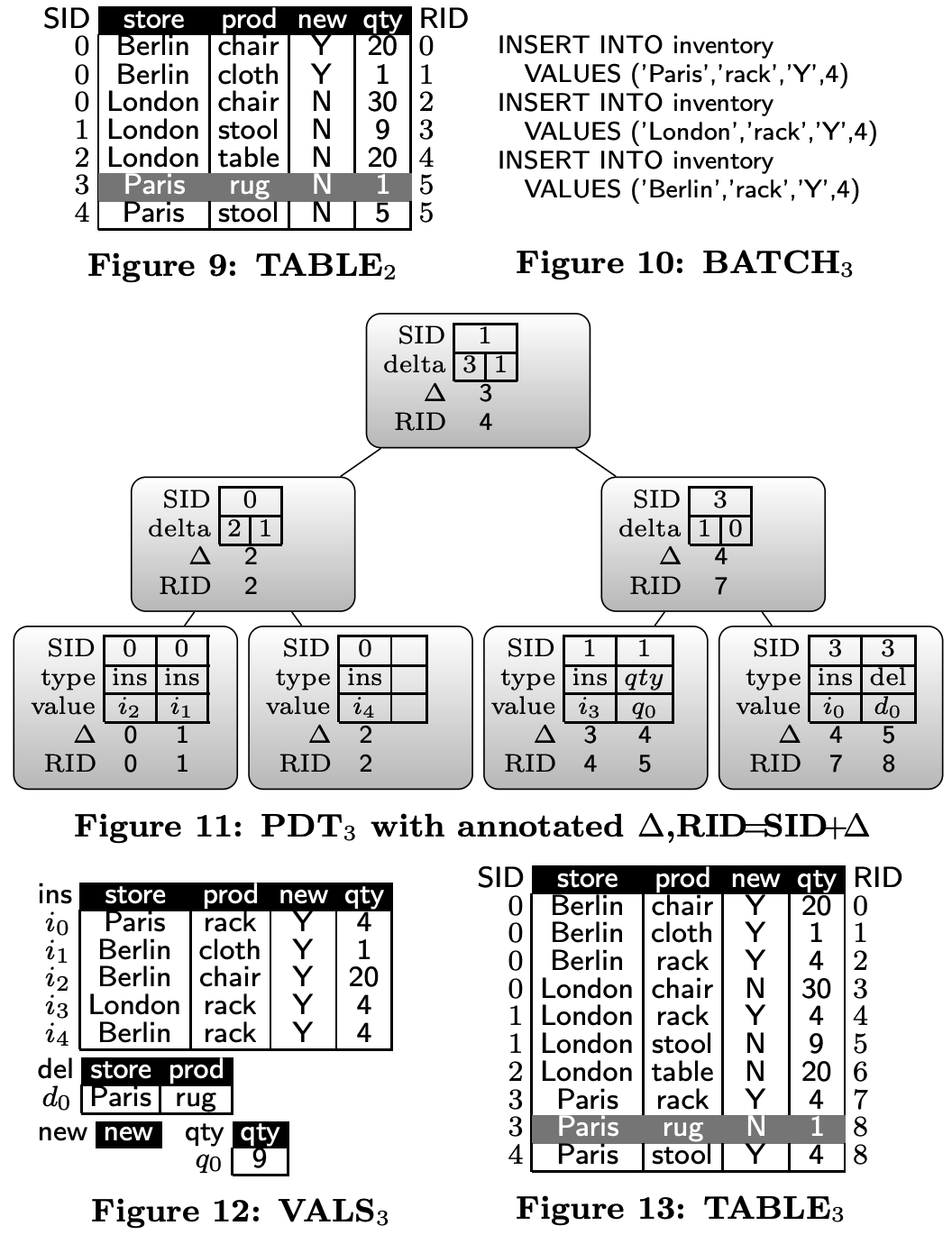
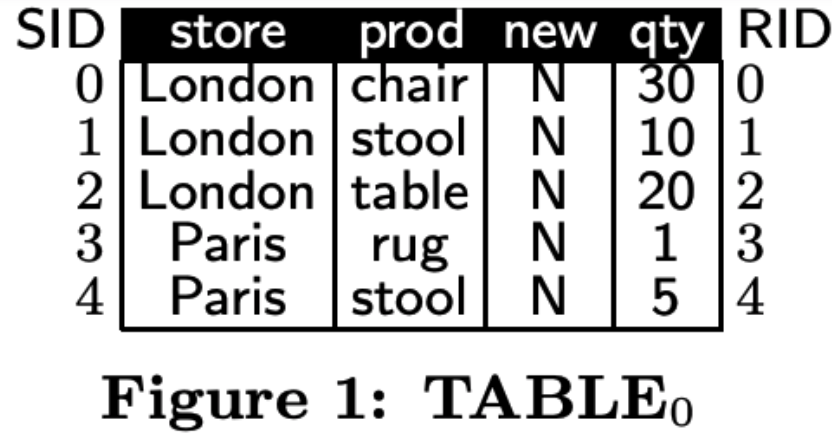
TABLE0
运行BATH1 (INSERT)
INSERT INTO inventory VALUES('Berlin', 'table', 'Y', 10)
INSERT INTO inventory VALUES('Berlin', 'cloth', 'Y', 5)
INSERT INTO inventory VALUES('Berlin', 'chair', 'Y', 20)
PDT1
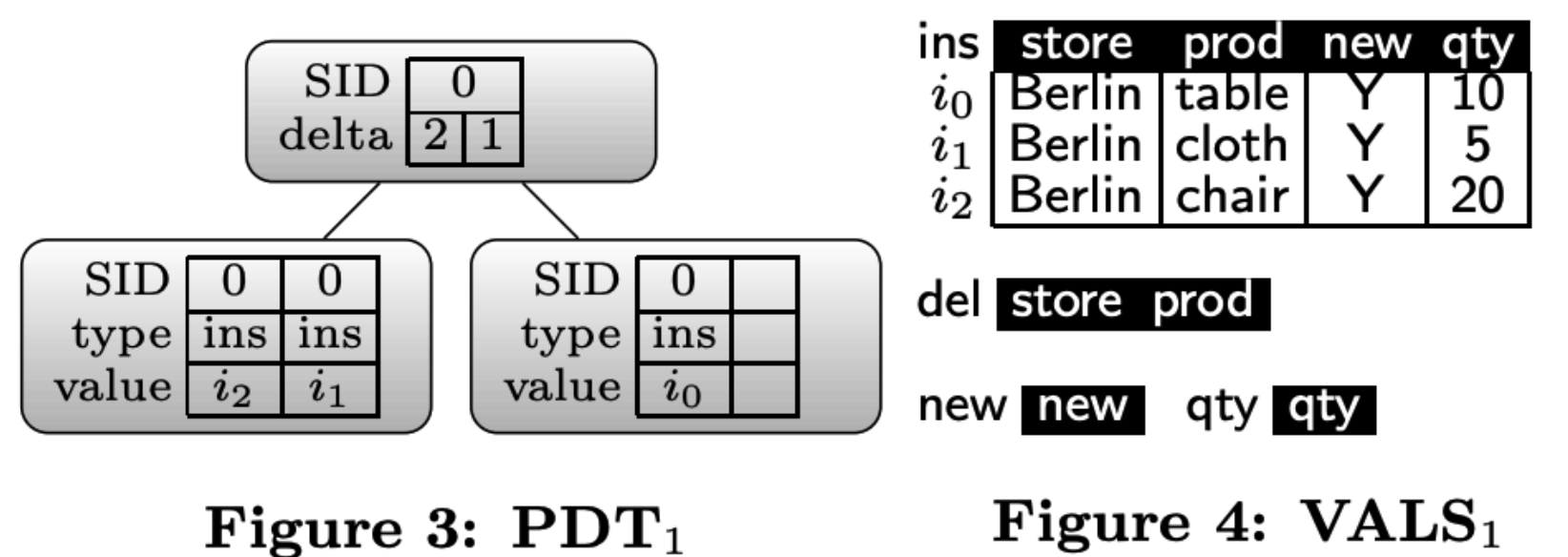
TABLE1
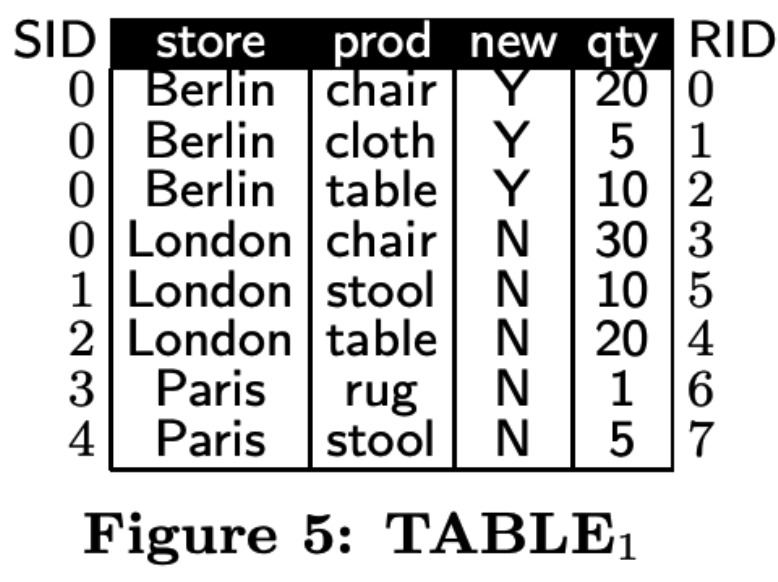
逻辑上TABLE0 + PDT1 === TABLE1
运行BATCH2 (UPDATE和DELETE)
UPDATE inventory SET qty=1 WHERE store='Berlin' and prod='cloth'
UPDATE inventory SET qty=9 WHERE store='London' and prod='stool'
DELETE FROM inventory WHERE store='Berlin' and prod='table'
DELETE FROM inventory WHERE store='Paris' and prod='rug'
PDT2
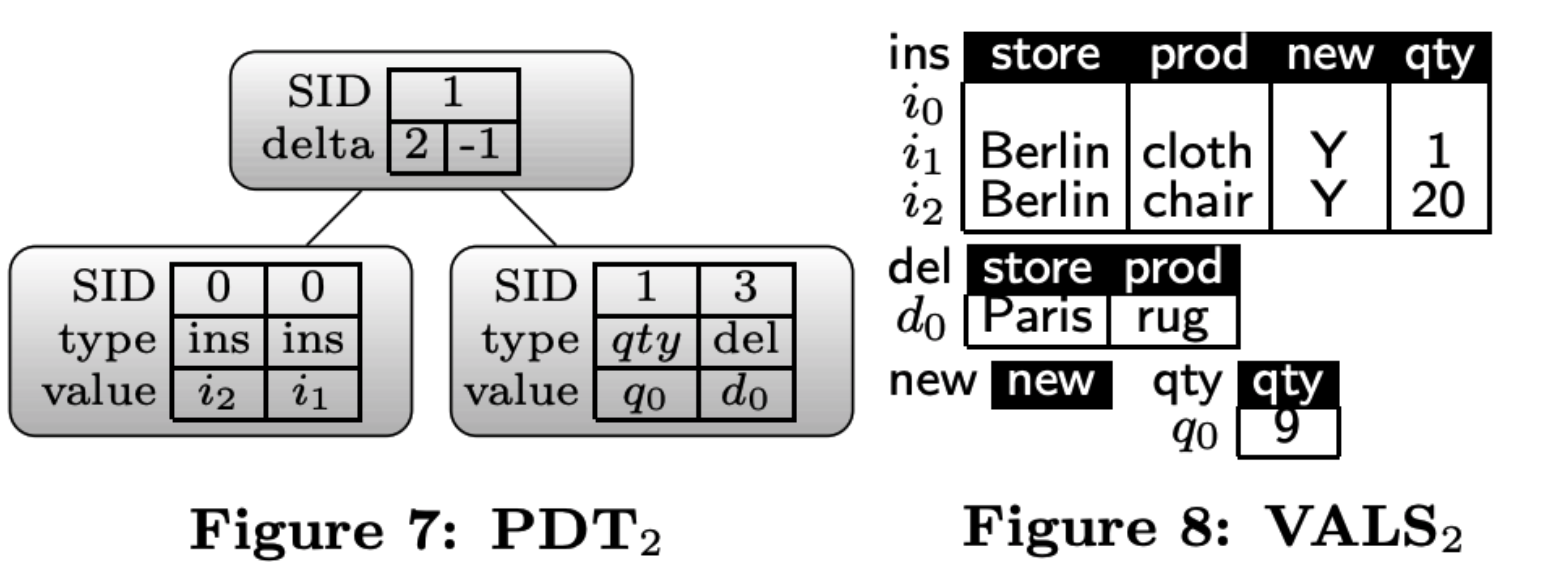
UPDATE inventory SET qty=1 WHERE store='Berlin' and prod='cloth',这句update的数据在PDT1中(ins=i1),因此直接修改VALS1中的数据。
UPDATE inventory SET qty=9 WHERE store='London' and prod='stool',这句update的数据在TABLE0中(SID=1、RID=1),因此在PDT2中创建一个节点(SID=1、type=qty、value=q0、q0=9)。
DELETE FROM inventory WHERE store='Berlin' and prod='table',这句delete的数据在PDT1中(ins=i0),因此直接删除i0的数据。
DELETE FROM inventory WHERE store='Paris' and prod='rug',这句delete的数据在TABLE0中(SID=3、RID=3),因此在PDT2中创建一个节点(SID=3、type=del、value=d0、d0={store: Paris, prod: rug})。
TABLE2
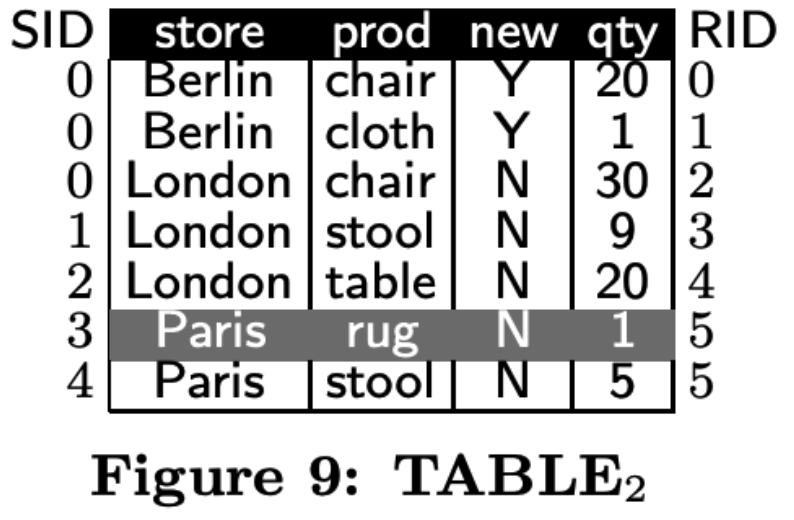
逻辑上TABLE1 + PDT2就等价于TABLE2
运行BATCH3 (INSERT)
INSERT INTO inventory VALUES ('Paris', 'rack', 'Y', 4)
INSERT INTO inventory VALUES ('London', 'rack', 'Y', 4)
INSERT INTO inventory VALUES ('Berlin', 'rack', 'Y', 4)
PDT3 + TABLE3
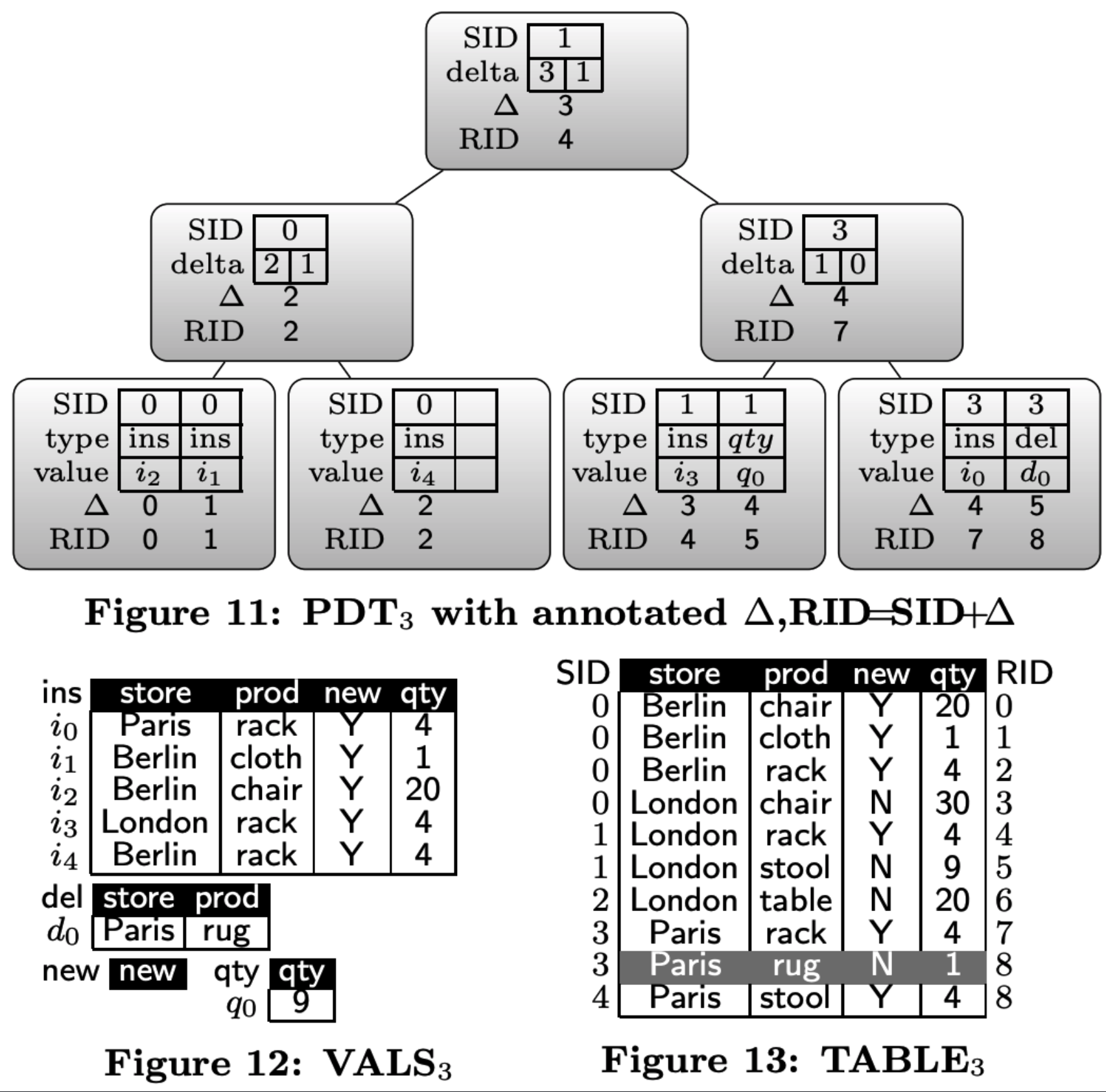
如何计算RID?
delta: 表示该节点左侧ins操作数量-del操作数据量
RID = SID + delta
参考
Written on August 22, 2019